Taurine for Mind and Body? Discover its Great Potential
Taurine has been getting a lot of attention recently and this is not by accident but because of the new studies that are coming out continuously the last years!
Introduction
Welcome to Happy Chemical, a website dedicated to promoting well-being and happiness through scientific knowledge. We are now launching a new section focusing on exploring the potential of natural compounds to enhance mood and overall performance. We will dive into the namely nootropics and check the science behind them.
You can use this section as a practical handbook.
However, remember that no material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Taurine – Our First Examined Compound
In this blog post, we delve into the remarkable world of taurine and its potential benefits for both the mind and body. At Happy Chemical, we believe in the significance of exploring compounds and their profound impact.

In a world filled with stress, anxiety, and mental health challenges, seeking solutions becomes increasingly important. This is where taurine comes into the spotlight.
But First Things First
Taurine, an amino acid-like substance, can be found naturally in various foods and is also produced by our own bodies. While it is commonly associated with energy drinks, taurine offers much more than a simple energy boost. Research suggests that taurine may play a crucial role in supporting cognitive function, reducing anxiety and stress, and promoting a sense of calmness and well-being.
What‘s the science behind taurine?
What are its properties?
How can it positively impact your mind and body?
Can taurine contribute to a happier, healthier life?
We’ll answer these questions and more! Empowering you with the understanding of how taurine can make a difference in your life. Let’s embark together on this journey.
What is Taurine?
Taurine’s composition
Taurine, a remarkable compound with diverse biological functions, has a unique chemical structure that sets it apart from other amino acids. Unlike protein-building amino acids, taurine does not contribute to protein synthesis. Instead, taurine is characterized by the presence of a sulfonic acid group (-SO3H) attached to its backbone. Hence it is classified as a sulfur-containing amino acid-like compound.
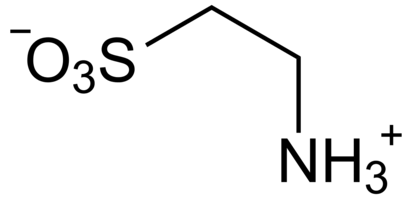
Natural Sources and Occurrence
This amino acid is naturally produced within our bodies, primarily in the liver and the brain. But it can also be obtained through various dietary sources.
Animal-based foods are particularly rich in taurine. Meats such as beef, pork, and poultry contain significant amounts of taurine, with higher concentrations found in organ meats like liver and heart. Seafood is another excellent source of it. Fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna are known to have high taurine content. Dairy products, such as milk and cheese, also contain moderate levels of this compound.
Plant-based foods generally have lower taurine content compared to animal sources. However, some legumes, including beans, lentils, and chickpeas, as well as certain grains like oats and brown rice, contain trace amounts of taurine.
And of course, we all know that taurine is the main ingredient of energy drinks, but also is used in some dietary supplements.
Main Body Functions of Taurine
This amino acid plays a vital role in various bodily functions, such as the following essential roles in key areas:
- Brain Health
- Cardiovascular Health
- Metabolism and Energy Production (Physical Performance)
- Immune System Support
Let’s explore some interesting stuff about them!

Brain Health
The examined compound is a key player in promoting brain health and optimizing cognitive function. We will describe this role in detail, but in general, it can be summarized below:
- Neurotransmission and Neuroprotection: Taurine acts as a neurotransmitter, facilitating communication between neurons. It also shields neurons from damage and promotes their survival.
- Cognitive Function and Memory: It improves cognitive function, memory, and learning abilities by enhancing synaptic plasticity and supporting the growth of new neurons.
- Mood Regulation and Stress Reduction: Our compound helps regulate neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation, reducing anxiety, stress, and symptoms of depression.
- Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects: Taurine’s antioxidant properties protect brain cells from oxidative stress. At the same time, its anti-inflammatory effects reduce inflammation linked to neurodegenerative conditions.
Cardiovascular Health
The correlation between taurine and cardiovascular health is significant. It seems that it supports cardiovascular function in several ways:
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Taurine promotes vasodilation, reducing resistance to blood flow and lowering blood pressure.
- Lipid Profile Management: It helps maintain a healthy lipid profile by reducing LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Electrical Signal Regulation: It regulates the electrical signals in the heart, promoting a regular heartbeat.
- Cardiac Muscle Health: Taurine supports the health and function of cardiac muscles, aiding in efficient blood pumping.
Metabolism and Energy Production (Physical performance)
Taurine is involved in various metabolic processes and energy utilization. Here’s a breakdown of how taurine impacts these processes:
- Fat Digestion and Absorption: It aids in the digestion and absorption of dietary fats.
- Fat Utilization and Energy Production: Taurine facilitates the transport and utilization of fats within cells. It promotes the entry of fatty acids into mitochondria, where they undergo beta-oxidation to produce energy-rich molecules like ATP.
- Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Regulation: Taurine supports insulin function, improving insulin sensitivity and promoting efficient uptake of glucose by cells. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Interestingly, Flávia G De Carvalho et al. suggest that taurine supplementation may increase lipid metabolism during high-intensity exercise!! Potentially resulting in the conservation of muscle glycogen stores.

Well, not exactly.
The point here is that the body starts to utilize easier fatty acids instead of the stored glycogen. This is called substrate switching. Substrate switching is when our body changes its preferred fuel source for energy production. Normally, it uses carbohydrates (glucose), but during fasting or intense exercise, it switches to burning fats for energy. This adaptation helps ensure a continuous energy supply for our body’s needs.
And this is very useful for people that are doing a low-carb diet or fasting. It is even greater for people who are doing CrossFit or similar types of exercise. Because during those stages you actually want your body to utilize energy using fat instead of glycogen.
Consequently, taurine contributes to metabolic health by optimizing fat digestion, utilization, and glucose regulation. It helps prevent metabolic imbalances and supports weight management. Not only these but also it seems to enhance physical performance and especially endurance. Some evidence that taurine reduces the lactate in human bodies through exercise, is a worth-trying factor!
Immune System Support
Taurine plays a role in supporting a healthy immune system. It enhances the function of immune cells, promoting their ability to defend against infections and pathogens. Taurine’s antioxidant properties also contribute to reducing inflammation and supporting overall immune health.
- Modulation of Immune Cells: Taurine regulates the activity of immune cells, enhancing their ability to eliminate pathogens and support a robust immune response.
- Regulation of Cytokines: It regulates the production and release of cytokines, important signaling molecules in immune responses. Cytokines prevent excessive inflammation.
- Antimicrobial Properties and Gut Health: Taurine exhibits antimicrobial effects, inhibiting the growth and activity of bacteria and viruses. Indeed, one of its metabolic byproducts plays an effective role in preventing the colonization of harmful bacteria, allowing beneficial “probiotic” bacteria to flourish. We all know the crucial role that gut microbiota plays in immune system function.
Taurine and Brain Chemistry
As we promised we will discuss in detail the brain chemistry of taurine. We are Happy Chemical, and when it comes to brain chemistry, we always have a lot of things to say.
Promoting Relaxation, Stress Reduction, and Improved Sleep
How can it do all of these? By modulating the activity of some neurotransmitters. Particularly, it seems that it has a significant effect on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
GABA is a neurotransmitter widely distributed in the central nervous system (CNS). It is known for its calming and inhibitory effects on the brain. For instance, in stressful or exciting conditions, GABA can act as an inhibitory agent to prevent the over-excitation of the neuron cells. In other words, when GABA interacts with the receptors of a neuron, it makes the neuron less likely to fire an action potential or release neurotransmitters.
- Relaxation: GABA helps to calm and relax the nervous system. When GABA levels are sufficient, it counteracts the effects of excitatory neurotransmitters. This creates a state of tranquillity and reduces feelings of anxiety.
- Stress Reduction: GABA helps regulate the body’s stress response by inhibiting the release of stress hormones and promoting a sense of calmness. This can lead to improved coping mechanisms, enhanced resilience, and a reduction in the negative effects of chronic stress.
- Improved Sleep Quality: GABA plays a crucial role in promoting healthy sleep patterns. It acts as a natural sedative, facilitating the transition into sleep and promoting deep, restorative sleep.

Taurine enhances the activity of GABA. Thus, it promotes relaxation, reduces stress, and contributes to improved sleep quality.
Stange, huh? Because we used to think of taurine as the main ingredient of energy drinks. But the truth is that those energy drinks don’t contain only taurine but also a significant quantity of caffeine. Hence, it is not the taurine that will keep you awake but caffeine.
Even though taurine might enhance your physical and mental performance. And this leads us to our next function, its cognitive effects.
Cognitive Function and Neuroprotective Effects
Taurine’s interaction with glutamate receptors holds promise for neuroprotection and enhanced cognitive function. Glutamate is referred to as the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. That means that when glutamate interacts with the receptors of a neuron it makes that neuron more likely to fire an action potential. By using this function glutamate is involved in synaptic plasticity. Through this, taurine plays its role in learning and memory.

In addition, by interacting with glutamate receptors, taurine can modulate their activity, leading to a balanced glutamate system. And this is important because glutamate, as an excitatory neurotransmitter, when present in excess, can lead to neuronal damage and neurotoxicity. This modulation is essential as excessive glutamate activity can lead to excitotoxicity. A phenomenon that is associated with neuronal damage and neurodegenerative disorders.
Taurine exerts its neuroprotective functions against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Hence, the interplay between taurine and glutamate receptors showcases the potential of taurine in promoting neuroprotection and brain health.
Does Taurine have antidepressant effects?
We are lacking efficient evidence but there is some indication that Taurine might have antidepressant effects. More specifically, Gao-Feng Wu et al. conducted a study on rats, not humans, where they investigated the preventive effects of it on depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress. What they found is very interesting.

In summary, they observed that taurine exhibited anti-depressant effects in 3 ways:
- By modulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal HPA axis, a complex system in our body that helps regulate our stress response.
- By regulating neurotransmitter levels such as serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and glutamate.
- By regulating neurotrophic factor expression, the namely “growth factors” of our neurons. They play a vital role in the development, maintenance, and survival of neurons, as well as in promoting their growth and communication with other cells.
Indeed, those are appealing findings. However, we emphasize again that more evidence is needed to be certain about the above effects!
Incorporating Taurine into Your Lifestyle
Disclaimer: The information provided in this section is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes or starting supplementation.
When it comes to reaping the potential benefits of taurine, incorporating it into your daily life can be a valuable addition to your well-being routine.
Here are some practical tips to help you incorporate taurine into your lifestyle:
Dietary Sources
- Animal-based foods: Consider including taurine-rich foods in your diet, such as beef, pork, poultry (especially organ meats like liver and heart), seafood (salmon, mackerel, tuna), and dairy products (milk, cheese).
- Plant-based options: While plant-based foods generally have lower taurine content, you can still include legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), certain grains (oats, brown rice), and other sources to supplement your taurine intake.

Supplementation
The recommended dosage of taurine can vary depending on factors such as age, health status, specific health goals, and individual needs. It’s important to note that no standardized dosage for taurine is established by regulatory authorities like the FDA.
However, to provide a general guideline, typical daily dosages of taurine for adults range from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day. This range can be divided into multiple doses throughout the day or taken as a single dose, depending on personal preference and individual response.
It’s worth noting that taurine is generally considered safe for most individuals when taken within recommended dosages. However, individual tolerance and sensitivity may vary, and some people may experience mild side effects such as stomach discomfort or diarrhea at higher doses. If you experience any adverse reactions, reducing the dosage or discontinuing use is recommended.
Nevertheless, if you decide to proceed with taurine supplementation always choose a high-quality brand. Select taurine supplements from reputable brands that prioritize quality and undergo third-party testing for purity and potency. Look for certifications or labels from regulatory authorities or independent testing organizations to ensure the product’s reliability.

Taurine supplements are available in various forms such as capsules, tablets, or powdered form. Follow the instructions on the product label or as advised by your healthcare professional.
Optimizing intake:
- Evaluate your current diet to determine if you are getting sufficient taurine from food sources. Then; consider the supplementation dosage you need.
- Taurine metabolism can be influenced by other nutrients such as vitamin B6, vitamin C, and zinc. Ensuring adequate intake of these cofactors will optimize the utilization of taurine in the body.
- The timing of supplementation is also important. Depending on your specific goals, you may consider timing your taurine supplementation strategically. For example, some individuals prefer taking taurine before workouts to potentially enhance exercise performance. Some others may find it beneficial to take it in the evening to support relaxation and sleep.
- Always pay attention! How does your body respond to taurine supplementation? Keep track of any changes in energy levels, mood, sleep quality, exercise performance, or other areas of interest.
- And of course, taurine will do nothing if you don’t give enough attention to the other healthy lifestyle choices. Engage in regular exercise, manage stress levels, prioritize sufficient sleep, and maintain a well-rounded approach to self-care.
Takeaway
And this was our first article on a nootropic. We, as Happy Chemical, by embracing the science behind a natural compound, aim to arm the readers with a deeper understanding of how this can positively impact their lives, or not!
In conclusion, Taurine, beyond its association with energy drinks, offers more than just an energy boost. It plays a vital role in supporting cognitive function, reducing anxiety and stress, and promoting a sense of calmness.
Its unique composition sets it apart from other amino acids. Naturally produced in our bodies and found in various foods, taurine is linked to key functions in brain health, cardiovascular health, metabolism, energy production, and immune system support.
Most importantly, its interaction with neurotransmitters like GABA highlights its role in relaxation, stress reduction, improved sleep, cognitive function, and neuroprotection.
While further research is needed on taurine’s potential antidepressant effects, preliminary studies suggest its ability to regulate neurotransmitter levels and influence mood regulation and depressive symptoms.
Indeed, incorporating taurine into one’s lifestyle can be a valuable addition to a well-being routine. Dietary sources, especially animal-based foods, and supplementation could both be good options for optimizing taurine intake.
However, always seeking professional medical advice is crucial before making dietary changes or starting supplementation. And of course, always choosing reputable brands that prioritize quality!
Did you find it helpful or interesting? Share it!
Also, go check out some of our articles, they deserve a reading!
Thanks for reading.
References
- F. G. De Carvalho et al. (2018). Taurine supplementation can increase lipolysis and affect the contribution of energy systems during front crawl maximal effort. Amino acids.
- Geo-Fang Wu et al. (2017). Antidepressant effect of taurine in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive rats. Scientific reports.
- J. A. Kurtz et al. (2021). Taurine in sports and exercise, Journal of Society of sports nutrition
- M. Waldron et al. (2018). The Effects of an Oral Taurine Dose and Supplementation Period on Endurance Exercise Performance in Humans: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Medicine.
- S. W. Schaffer et al. (2001). Physiological roles of taurine in heart and muscle. Journal of biomedical science.
- J. Y. Wu and H. Prentice (2010). Role of taurine in the central nervous system. Journal of biomedical science.
- S. Schaffer and H. W. Kim (2018). Effects and Mechanisms of Taurine as a Therapeutic Agent. Biomolecules and Therapeutics.



Nootropics for Brain Fog: Do Smart Drugs Really Work? - Happy Chemical
August 26, 2023 @ 9:17 am
[…] have already discussed taurine’s huge potential in our recent post: Taurine for Mind and Body? In summary, we can say that among others […]